Compare and Contrast the Structure of Yeast and Algae
Discuss the role of specific algal and fungal toxins in human disease. Compare and contrast the structure of a vein and artery.

Difference Between Algae And Fungi Table Easy Biology Class
Some molds are vibrant whereas yeast is colorless.

. Yeast and Molds both belong to the kingdom fungi are eukaryotic microorganisms but yeast is single-celled organisms which reproduce asexually mainly by binary fission or budding whereas Molds are multicellular reproduce sexually or asexually. Fungi are a group of unicellular or multinucleate organisms that live and grow on decomposed matter. In yeast there are several linear DNA.
Ø Both algae and fungi are thallophytes plant body not differentiated into root stem and leaves Ø Both algae and fungi are placed together in the division thallophyta of cryptogams. In yeast 80s ribosomes are present. Algae are plant-like unlike the fungi.
The algee is strong and the yeest is thecher. Like fungi some algae ie. Yeast is unicellular whereas mould is multi-cellular.
Compare and contrast the structure of yeast and algae. Mold is reproduce sexually and asexually by the use of sores whereas yeast is reproduced asexually by the tactic of mitosis. Request PDF Compression Testing and Modeling of Spherical Cells - Comparison of Yeast and Algae The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the.
Ø Vascular tissue system is. It is the causative agent of vaginal yeast infections as well as oral thrush a yeast infection of the mouth that commonly afflicts infants. The yeasts are unicellular fungi.
Bacterium are single celled micro-organisms that belong to the group of Prokaryotics. There are multiple cell walls algae have a cellulose cell wall fungi and yeast have chitin cell walls protozoa have pellicle cell walls and animals do not have a cell wall instead they have a plasma membrane covered by glycocalyx. Up to 24 cash back Algae are photosynthetic organisms which contain chlorophyll.
Most widespread strategy of yeast copy is budding. Kingdom Protista composes of unicellular plants algae and unicellular animals. A the factors that stimulate their formation b their structure and c their function.
This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of cell structure of yeast. Explain what is meant by the SIN-SON illustration. Albicans has a morphology similar to that of coccus bacteria.
Unicellular animals are classified as protozoa. The cells are extremely variable in shape being globose oval elongated or rectangular. A mutualistic combination of an alga or a cyanobacteria and a fungus.
Algae mostly thrive in or underwater whereas fungi grow on land. How is the structure of veins and arteries related to their fuction. Compare and contrast protozoan cysts fungal spores and bacterial endospores with regard to.
Ø With the exception of blue green algae majority of algae and fungi are eukaryotic. Compare and contrast the structure of yeast and algae. Algae are photosynthetic organisms that possess photographic pigments such as chlorophyll.
However yeast is a eukaryotic organism note the nuclei and is much larger. In bacteria nucleolus is absent and in yeast nucleolus is present inside the nucleus. By fungi which allow digestion to take place outside of the fungal body Along with bacteria fungi which include yeast bread mold and mushrooms are considered to be the decomposers of the.
Similarities between Algae and Fungi. Cells may remain attached in short chains forming a pseudomycelium but they do not produce true mycelium. Compare and contrast glycocolyx plasma membrane and cell wall Eukaryotic cell walls are simple in structure compared to prokaryotic cell walls.
Each structure had a nitrogen-nitrogen bond length of 167 120 and 110. In bacteria 70s ribosomes are present. There are 1500 types of yeast present and commonly found in fruits vegetables on the skin of.
In return the fungus provides a holdfast for the alga. They were the biologic ancestors of many of todays higher plants. In bacteria there is only a single circular DNA.
If you were to compare the mass of the products and reactants in a reaction you would find that the mass of the products is alw 9 2 answers Draw all three possible lewis dot formulas for N2O. Candida albicans is a unicellular fungus or yeast. Alga are a group of simple typically autotrophic organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms.
Kingdom fungi contain molds and yeasts. Compare and contrast the morphology of Cestodes Trematodes and Nematodes. The alga photosynthesizes providing a carbs for the fungus.
The key difference between fungi and protozoa is that the fungi are mainly multicellular eukaryotic organisms while protozoa are unicellular eukaryotic organisms. Describe the roles of fungi and algae in a lichen. Seaweed and fresh water moss are types of algae.
Yeast affect these with compromised immune. Required fields are marked. In contrast parasites are fungi which obtain nutrients directly from a living host.
List the defining characteristics of an algae. Yeast are eukaryotic single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. Bacteria are single celled micro-organisms that have a varied range of.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Algae are photosynthetic organisms that possess photographic pigments such as chlorophyll. Mushrooms yeast truffles are types of fungi.
Compare and contrast the structure of yeast and algae. Your email address will not be published. Yeast are eukaryotic single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom.
In bacteria there is no organized nucleus and in yeast there is an organized nucleus. Alga are Eukaryotic organisms unicellular or multi-cellular that contain chlorophyll and carry out the process of photosynthesis.

Bioengineering Free Full Text Cyanobacterial Pha Production Review Of Recent Advances And A Summary Of Three Years Working Experience Running A Pilot Plant Html
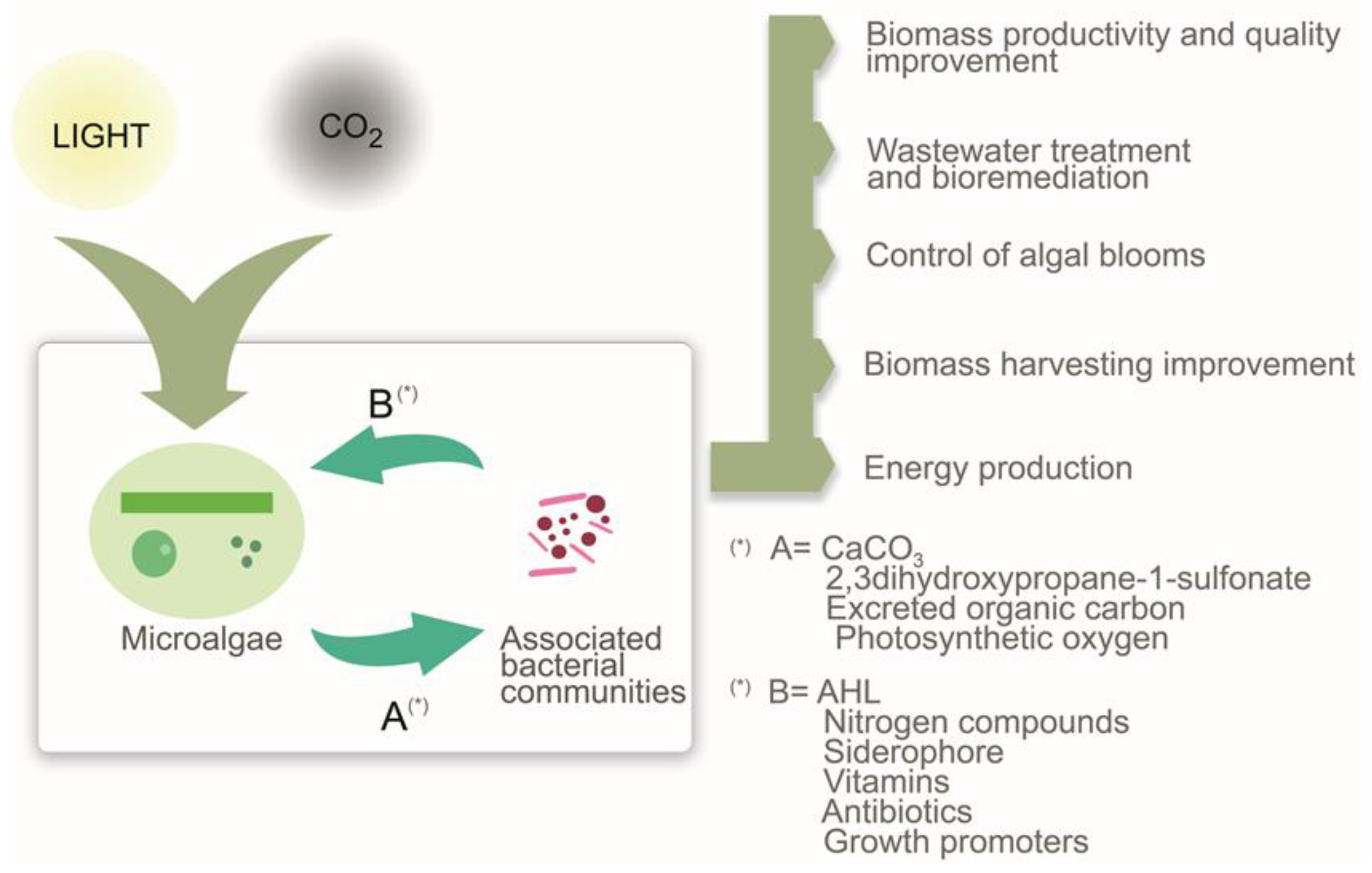
Marine Drugs Free Full Text Impact Of Microalgae Bacteria Interactions On The Production Of Algal Biomass And Associated Compounds Html

Difference Between Algae And Fungi Are Explained In Detail
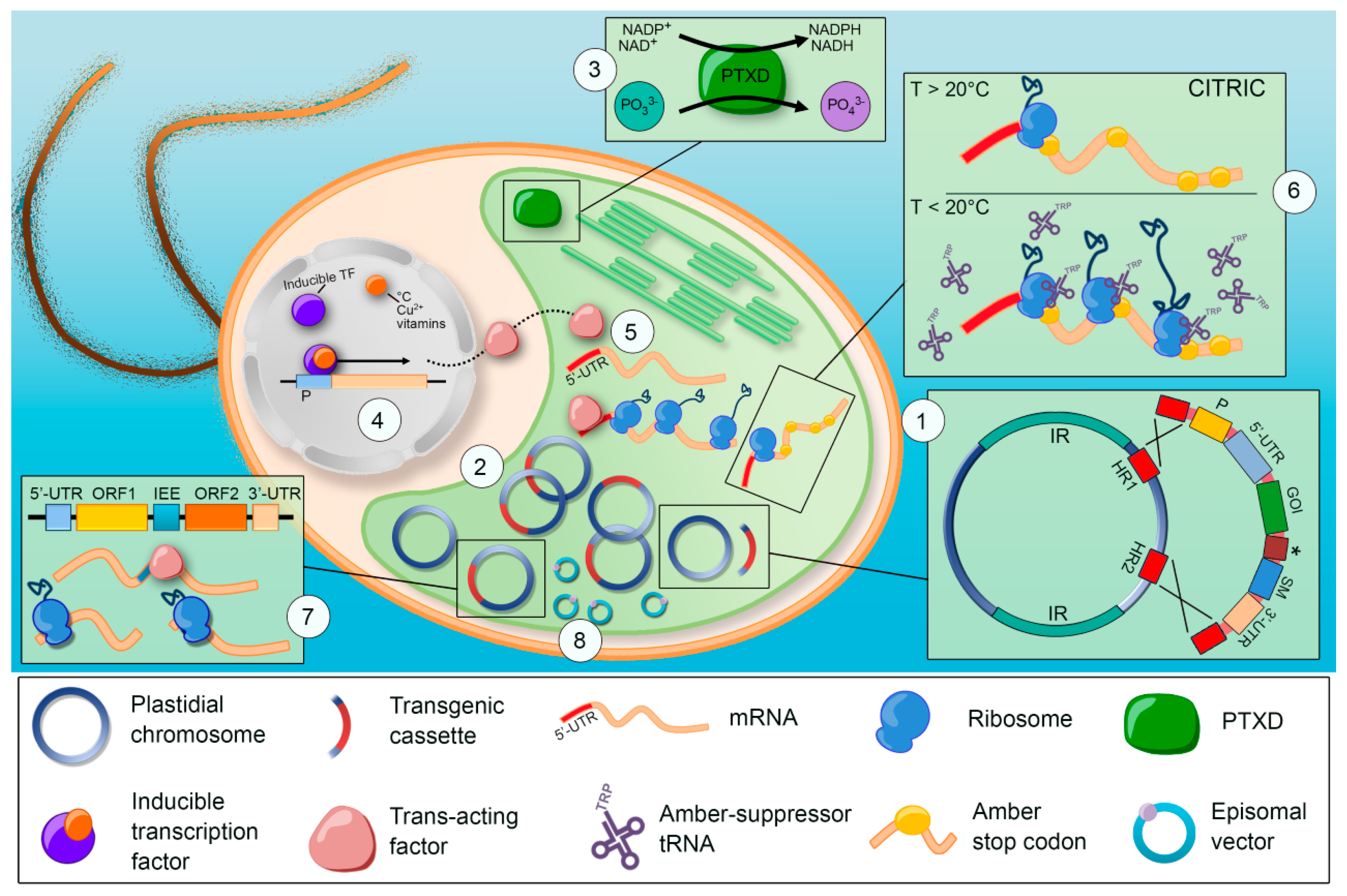
Microorganisms Free Full Text Harnessing The Algal Chloroplast For Heterologous Protein Production Html

Multiproduct Microalgae Biorefineries Mediated By Ionic Liquids Trends In Biotechnology

Structure And Function Manoa Hawaii Edu Exploringourfluidearth
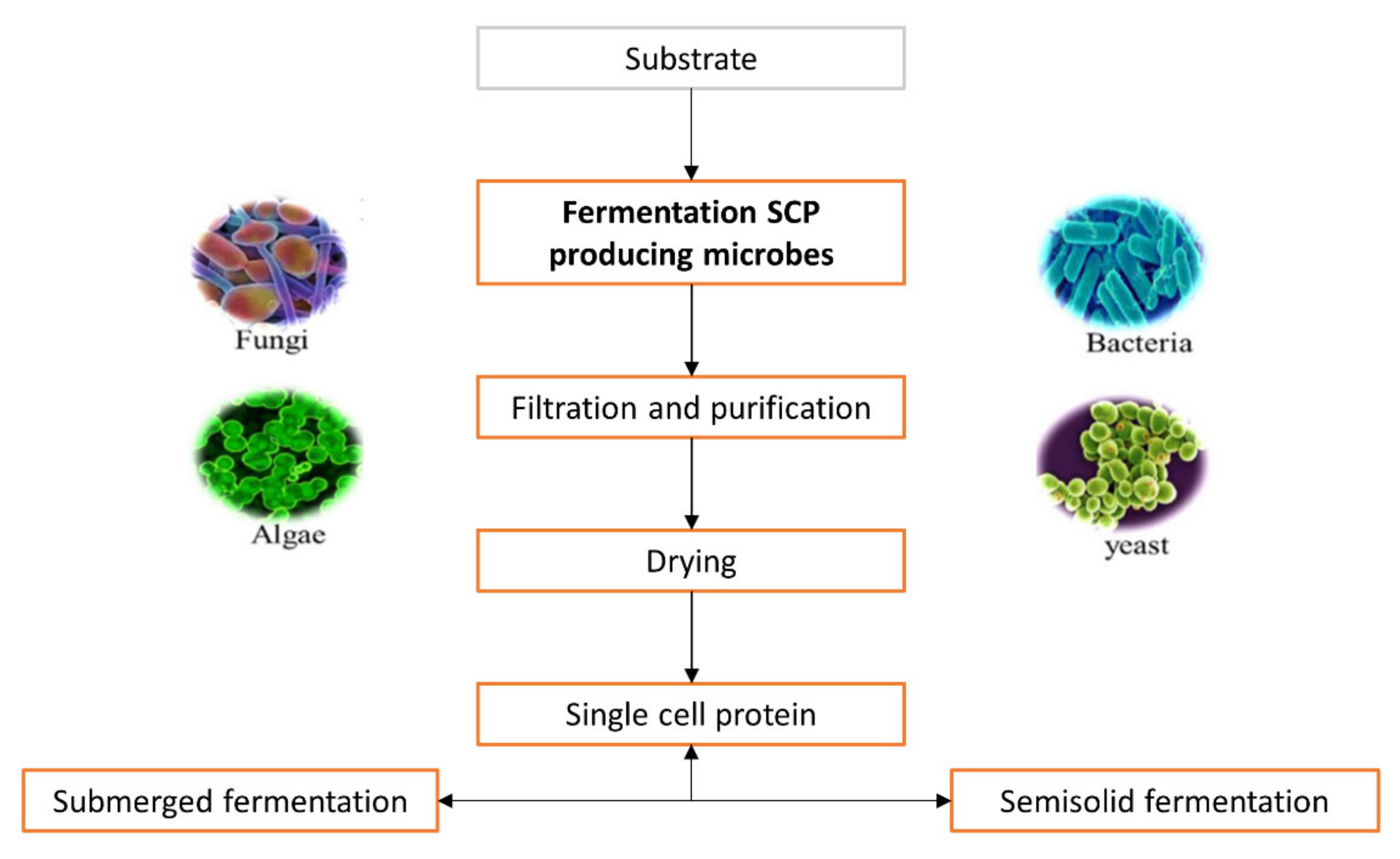
Sustainability Free Full Text Single Cell Protein A Potential Substitute In Human And Animal Nutrition Html

Comparison Of Scp Production From Algae Fungi And Bacteria Singh 1998 Download Scientific Diagram

De Novo Organelle Biogenesis In The Cyanobacterium Tdx16 Released From The Green Alga Haematococcus Pluvialis Biorxiv

Difference Between Algae And Fungi In Tabular Form
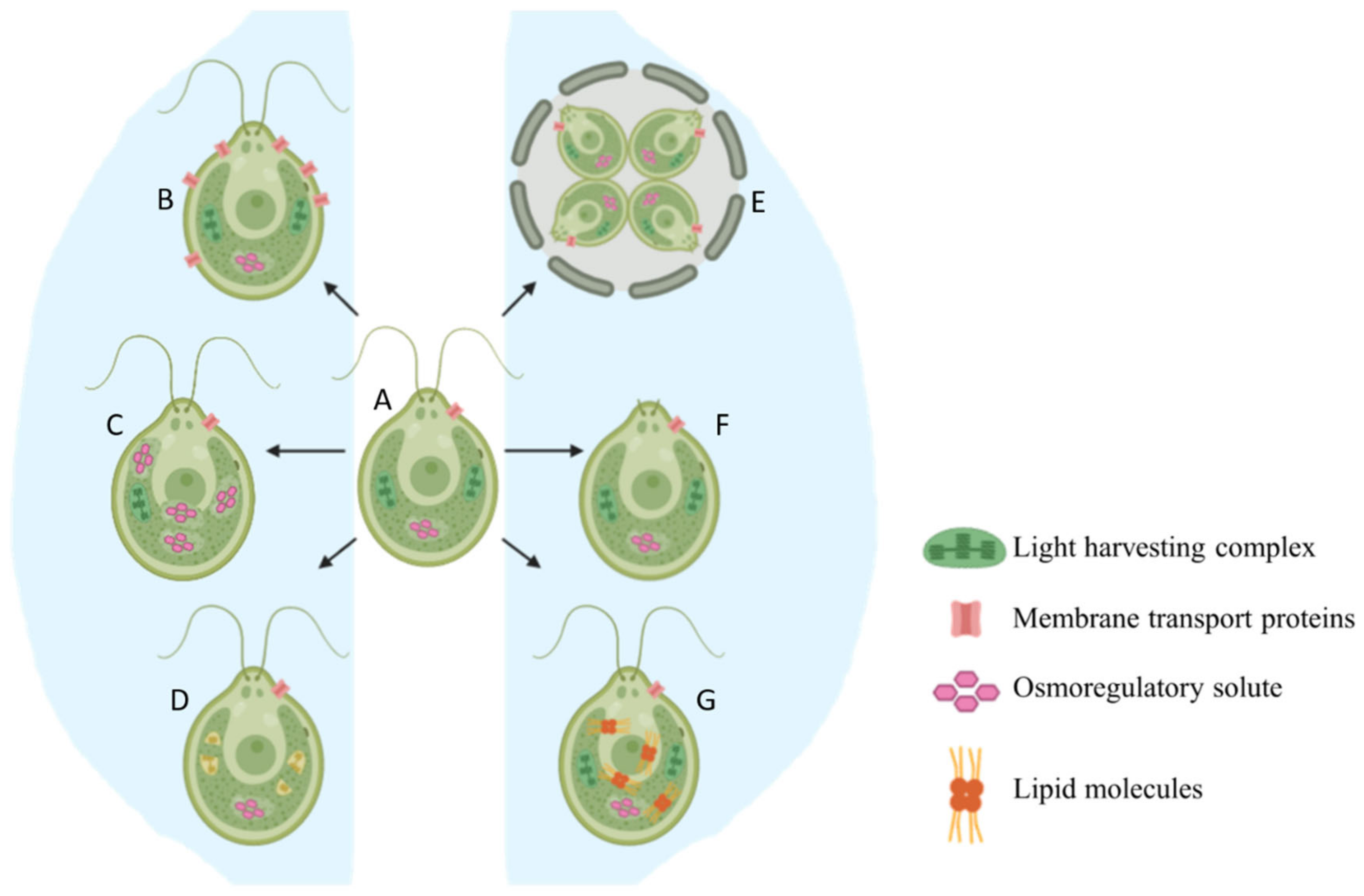
Cells Free Full Text Salinity Stress Responses And Adaptation Mechanisms In Eukaryotic Green Microalgae Html

Structure And Function Manoa Hawaii Edu Exploringourfluidearth

Unicellular Organism Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Lignocellulosic And Algal Biomass For Bio Crude Production Using Hydrothermal Liquefaction Conversion Techniques Mechanism And Process Conditions A Review
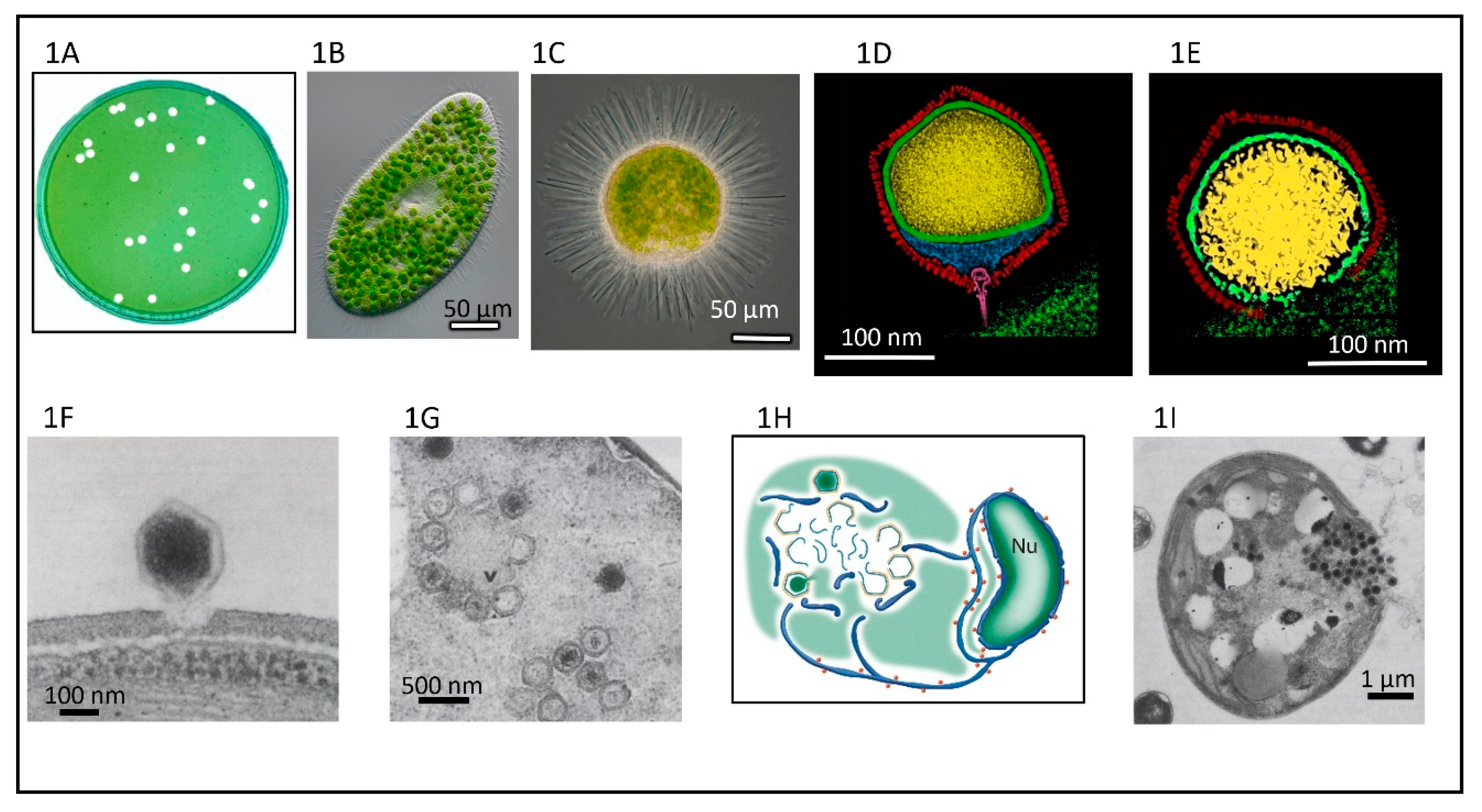
Viruses Free Full Text Chloroviruses Html

Schematic Representation Of Algal Evolution With Respect To Pt Nuclei Download Scientific Diagram
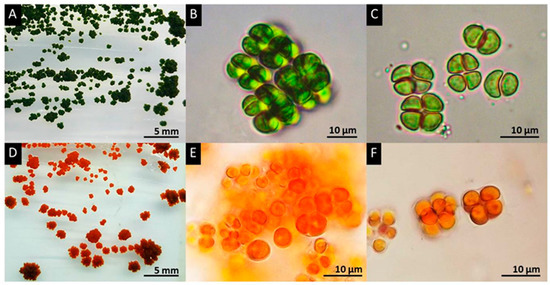
Biology Free Full Text Detection And Enhancement Of Ketocarotenoid Accumulation In The Newly Isolated Sarcinoid Green Microalga Chlorosarcinopsis Py02 Html

Comments
Post a Comment